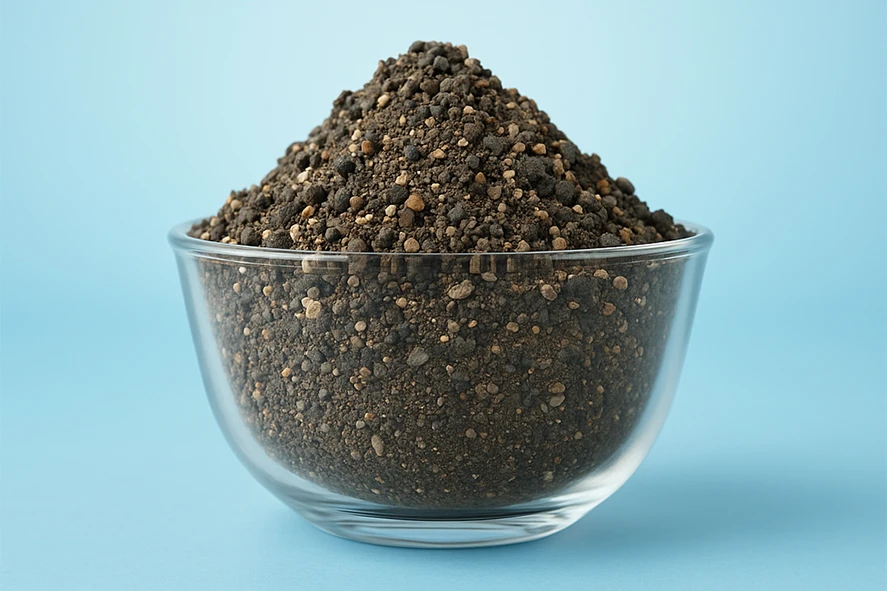
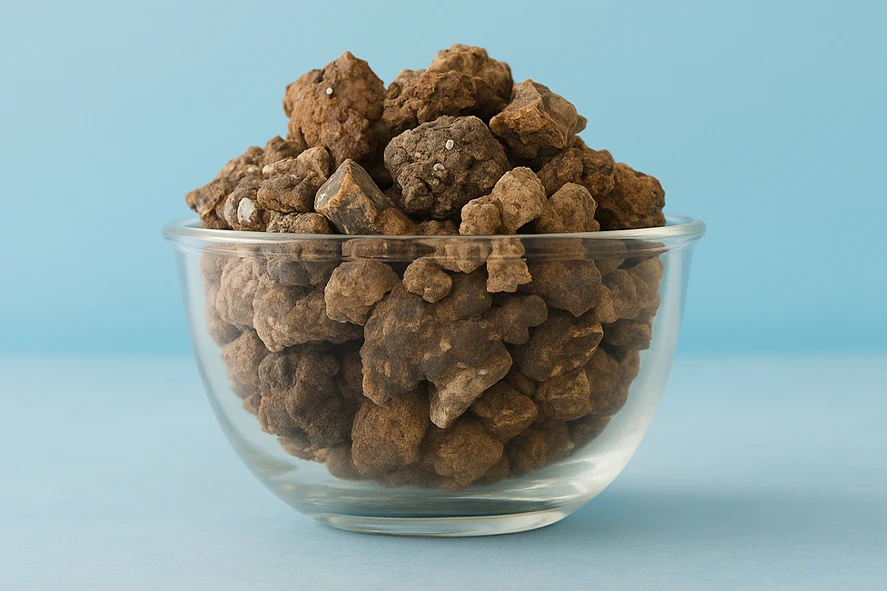
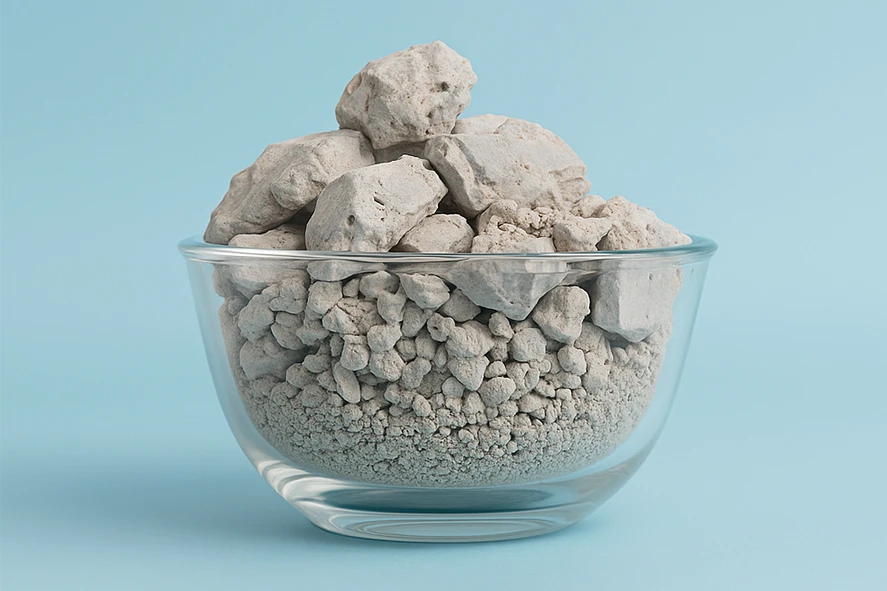
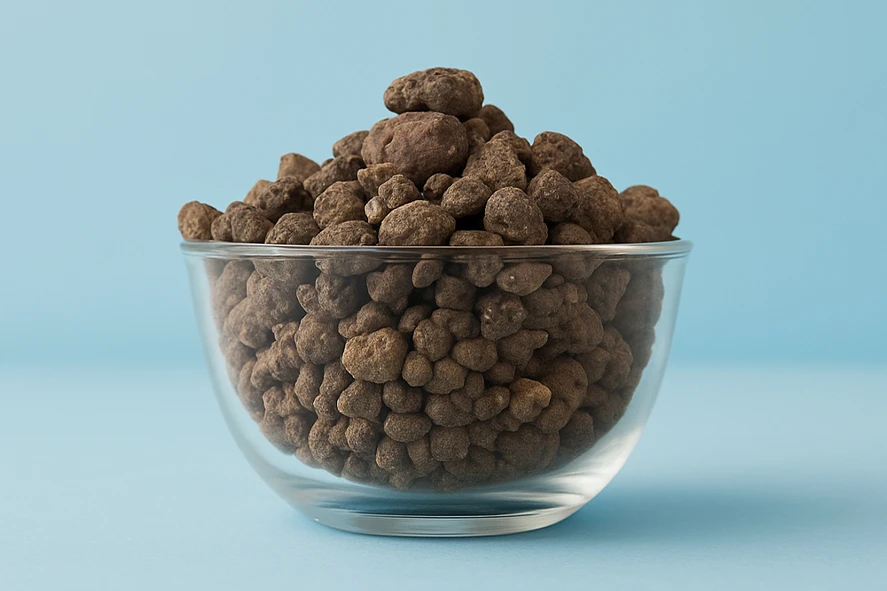
Refractory Clay
Refractory clay
Refractory clay or Calcined Clay is obtained by calcining (heating) superior-grade clay at high temperatures from 850 to 1600 Celsius. This process removes moisture and volatiles as well as increases the alumina content.
For ceramics, typical chamotte contains 40% minimum alumina, 30% minimum silica, 4% maximum iron oxide, and up to 2% calcium oxide and magnesium oxide combined. The particle size distribution is generally coarser in size than the other raw materials used to prepare sanitaryware bodies for instance.
For refractories, chamotte contains from 38% to 48% alumina in general. Iron is generally limited to 2.5% and alkalies must be also limited in amount to preserve refractoriness and thermal stability at temperatures up to 1400°C.
It has a higher alumina content of 40% to 60%, whereas raw clay has an alumina content of 30% to 40%. The Calcination is carried out in rotary kilns at different temperatures ranging from 850 to 1600 Celsius, depending upon the customer's application.
Chamotte grains have been treated at very high temperatures, which means that they will be stable when fired at a slightly lower temperature. They are used to make up the rigid skeleton of ceramics and refractories at high temperatures, limiting shrinkage due to sintering.